Like most other stars, Betelgeuse is composed of gas and dust particles which cooled over time, giving the star a red-orange color. Similarly, just like the life cycle of any other star, Betelgeuse is found with hydrogen, helium, carbon, oxygen, and heavier element up to iron. Up to now, the red supergiant is 10 million years old compared to the 5 billion years old of our sun. The surrounding of Betelgeuse looks brighter than the regions further out, indicating that the star started shedding its mass in a faster rate at about 30,000 years ago. Betelgeuse's probable future is that it will explode as a supernova and all the heavier elements will emit for future stellar generations. The ejected outer layer, known as the bow shock, will form an arc curve until it hits surrounding materials. However, the actual explosion time is still unsure. It could happen any day, now or a few hundred thousand years later. By then, the explosion may be big enough that the light emitted will travel to earth to look like a second sun for a few days.

elements in Betelgeuse
Betelgeuse Supernova explosion. the bow shock is an arc-structure force
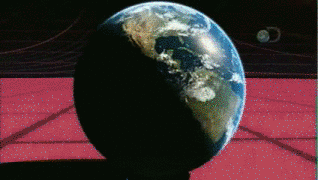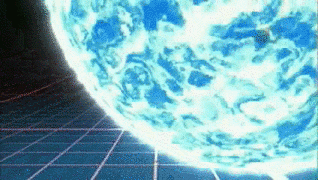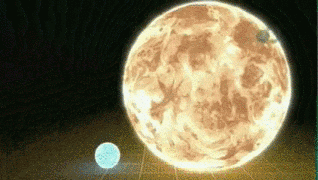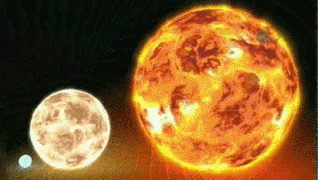
Scientist believes that Betelgeuse will explode in 100,000 years, but this number is still uncertain
When the star explodes, it will look like there are 2 suns like this image from Star Wars.
Works Cited
"Betelgeuse."
Herschel Space Observatory. Astronomy&Astrophysics, 22 Jan. 2013. Web. 14 Dec. 2014.
LINK
"Betegeuse -- The Red Supergiant 100,000 Times Brighter than Our Sun: An Emerging Supernova."
The Daily Galaxy. Great Discoveries Channel, 21 July. 2013. Web. 14 Dec. 2014.
LINK
Gardner, David. "Earth 'to Get Second Sun' as Supernova Turns Night into Day."
Mail Online. Associated Newspapers, 10 Mar, 2011. Web. 14 Dec. 2014.
LINK
"Meet the Workaholic Star, Betelgeuse."
Night Sky Network. NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory, n.d. Web. 14 Dec. 2014.
LINK




.jpg)








.jpeg)